This cheat sheet is based on the theoretical foundation developed in my Nand2Tetris Boolean Logic article.
Table of contents
Open Table of contents
What is boolean algebra
Boolean algebra uses binary values:
0= false1= true
It replaces arithmetic operators with logical operators, and is the basis for all digital circuits.
Basic operators
| Operation | Symbol | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOT | ~ | Inverts the input | ~1 = 0 |
| AND | & | True only if both inputs are true | 1 & 1 = 1 |
| OR | | | True if at least one input is true | 1 | 0 = 1 |
| XOR | ^ | True if inputs are different | 1 ^ 0 = 1 |
Figure 1: Different boolean operations.
Truth tables
A truth table is a table that shows the truth value of each possible combination of inputs.
AND gate
| x | y | Output |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Figure 2: Truth table for the AND operation.
OR gate
| x | y | Output |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Figure 3: Truth table for the OR operation.
XOR gate
| x | y | Output |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Figure 4: Truth table for the XOR operation.
Fundamental laws
Identity
A & 1 = AA | 0 = A
Null
A & 0 = 0A | 1 = 1
Idempotent
A & A = AA | A = A
Complement
A & ~A = 0A | ~A = 1
Commutative
A & B = B & AA | B = B | A
Associative
(A & B) & C = A & (B & C)(A | B) | C = A | (B | C)
Distributive
A & (B | C) = (A & B) | (A & C)A | (B & C) = (A | B) & (A | C)
Special laws
De Morgan’s laws
~(A & B) = ~A | ~B~(A | B) = ~A & ~B
Used to transform expressions to NAND/NOT form.
Absorption law
A & (A | B) = AA | (A & B) = A
Simplification techniques
Algebraic simplification
Apply identities and laws above to reduce complexity.
Karnaugh Maps (K-Maps)
A graphical method to group minterms and simplify boolean expressions.
- Use Gray code to layout variables.
- Group 1s and “don’t care” in powers of 2 (1, 2, 4…).
- Each group = simplified term.
- Final expression: OR of all groups.
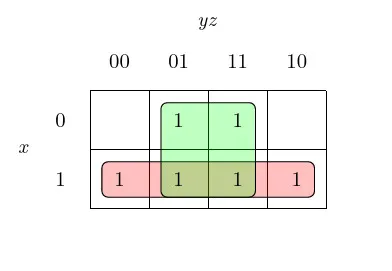
Figure 5: The Karnaugh map for the function x+z.
Useful links
Appendix: Selected proofs
This section contains a few representative proofs for readers interested in the logical foundations of Boolean algebra. Each proof uses either a truth table or simple algebraic reasoning.
De Morgan’s laws
Law 1
~(A & B) = ~A | ~BProof:
| A | B | A & B | ~(A & B) | ~A | ~B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
The column for ~(A & B) is the same as the column for ~A | ~B.
Law 2
~(A | B) = ~A & ~BProof:
| A | B | A | B | ~(A | B) | ~A & ~B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Again, ~(A | B) and ~A & ~B have identical outputs.
Absorption law
A & (A | B) = A
A | (A & B) = AAlgebraic proof:
A & (A | B) = (A & A) | (A & B) = A
A | (A & B) = (A | A) & (A | B) = A